Transmitted light microscopy is the general term used for any type of microscopy where the light is transmitted from a source on the opposite side of the specimen to the objective lens.
Transmitted light microscopy optical pathways.
This tutorial explores the optical pathways in a transmitted light microscope.
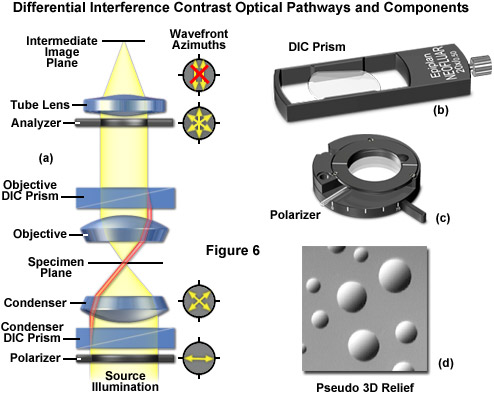
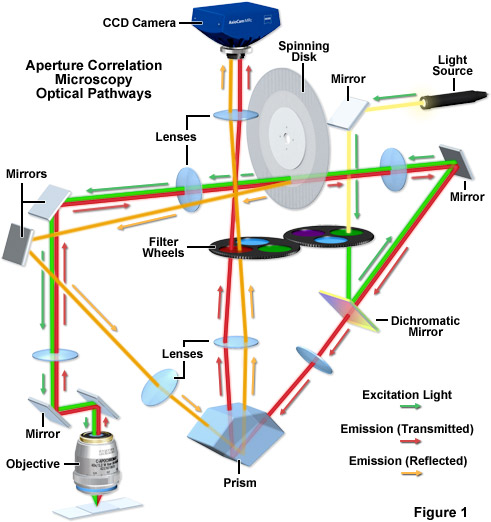
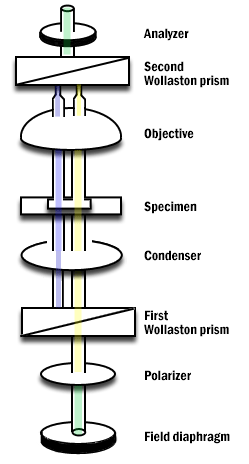
We present a new set of symmetrical ray diagrams of the optical pathways in transmitted reflected and epifluorescence light microscopes equipped with infinity corrected optics.
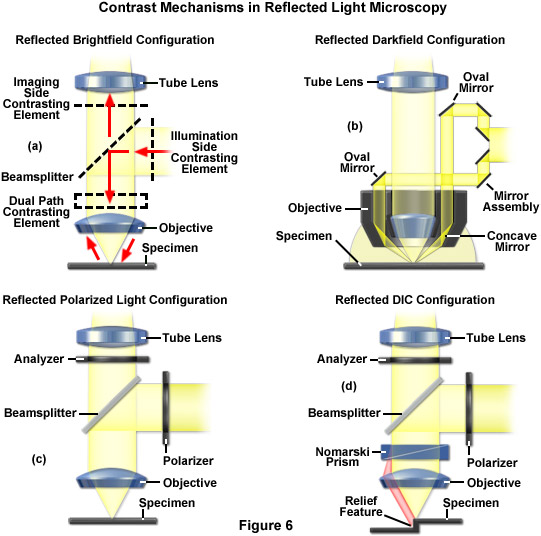
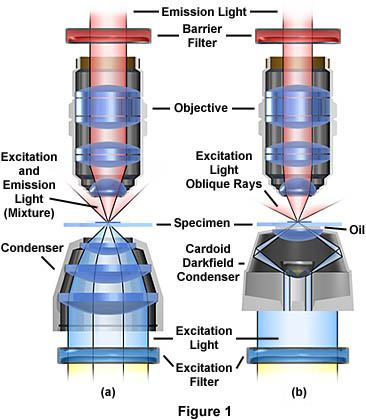
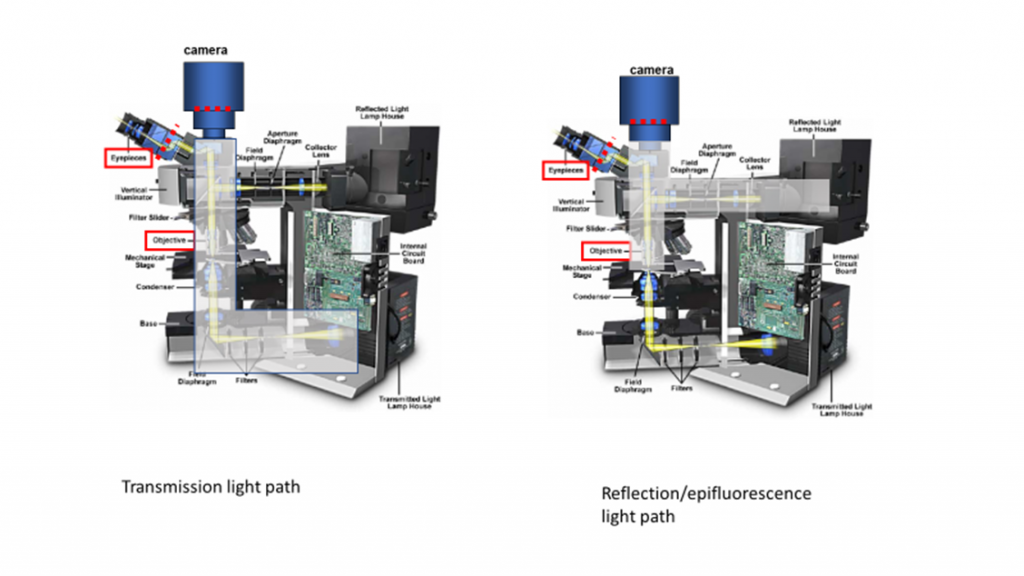
The optical pathway for reflected light begins with illuminating rays originating in the lamp housing for reflected light the upper housing in figure 2.
Instructions and a discussion about how to operate this tutorial appear immediately below the window.
A typical microscope configured for both types of illumination is illustrated in figure 2 the transmitted light source and optical pathway is not shown in this illustration.
It is intended that.
To operate the tutorial use the slider bars beneath the microscope to control the aperture of the field diaphragm left slider the aperture condenser diaphragm.
Optical microscopes are the oldest design of microscope and were possibly invented in their present compound form in the 17th century.
There are numerous light sources available to illuminate microscopes both for routine observation and critical photomicrography.
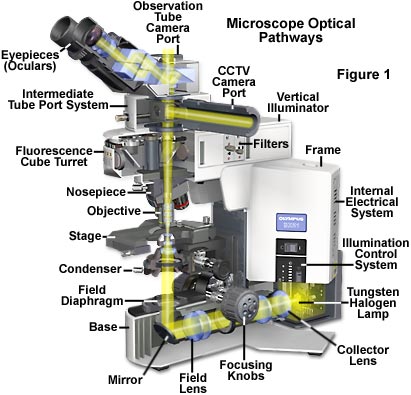
A most common light source because of its low cost and long life is the 50 or 100 watt tungsten halogen lamp as illustrated at the base of the microscope diagram in figure 1 which also details the optical pathways in a typical modern transmitted light microscope.
Background of similar intensity.
Illumination of the specimen is the most important controllable variable in achieving high quality images in microscopy critical photomicrography and digital imaging.
Today many microscope manufacturers offer advanced models that permit the user to alternate or simultaneously conduct investigations using both vertical and transmitted illumination.
Instructions and a discussion about how to operate this tutorial appear immediately below the window.
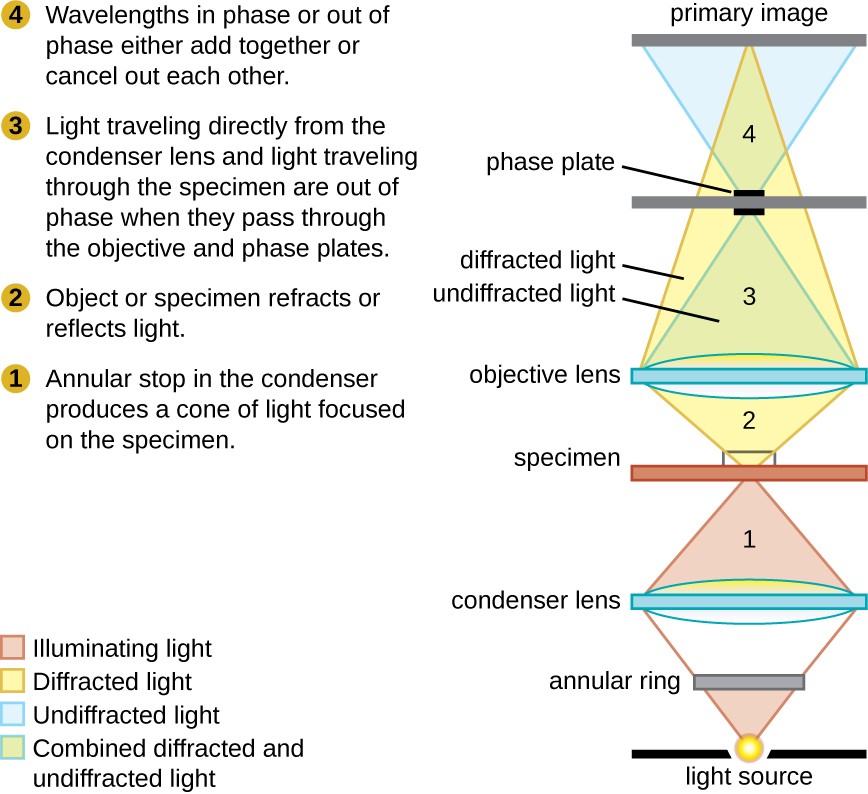
Usually the light is passed through a condenser to focus it on the specimen to get maximum illumination.
The optical pathway for reflected light begins with illuminating rays originating in the lamp housing for reflected light.
Transmitted light microscopy optical pathways.
Optical pathways in the transmitted light microscope the design of an optical microscope must ensure that the light rays are organized and precisely guided through the instrument.
The optical microscope also referred to as a light microscope is a type of microscope that commonly uses visible light and a system of lenses to generate magnified images of small objects.
Basic optical microscopes can be very simple although many complex.